A new analysis indicates that climate change is breaking alarming records all across the world.
The World Meteorological Organization’s (WMO) report, State of the Global Climate 2021, recounts a slew of extreme weather events last year and warns that early warning systems are now “essential” for helping industries adapt to climate change.
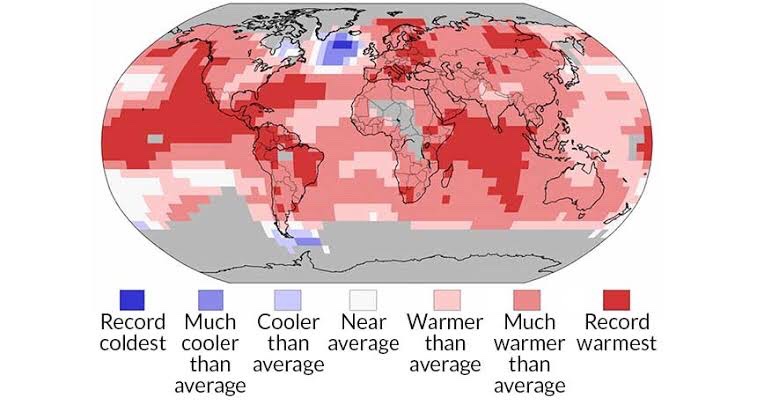
The world had 5th warmest April on record (tied).@NOAA map shows main features.
— World Meteorological Organization (@WMO) May 13, 2022
Intense #heatwave in #India and #Pakistan (still continuing) and record-breaking rain in #SouthAfrica
WMO #StateofClimate 2021 report 18 May has more info on extreme weather and climate events. pic.twitter.com/PYEMOR2EP2
Of course, global warming has been smashing records for some years. NASA and the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration of the United States reported in 2020 that the decade 2010 to 2019 was the hottest since records began in the late 1800s.
In 2019, carbon emissions from fossil fuels reached a new high. The UN also revealed that a new record high temperature of 18.3C was achieved in the Antarctic in 2021.
According to the World Meteorological Organization (WMO), the world surpassed eight climate change records in 2021.
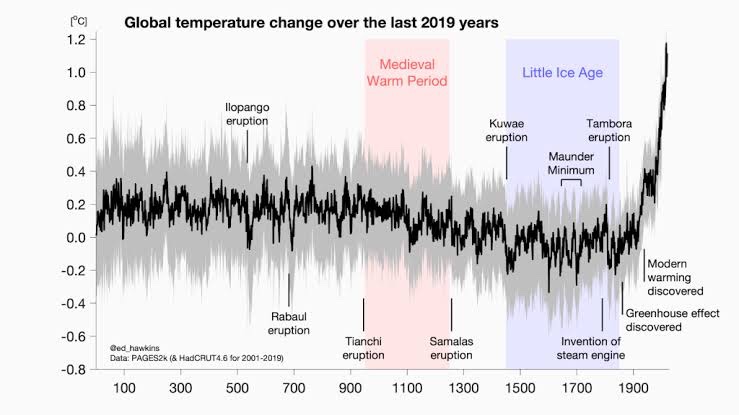
The WMO has cautioned that the last seven years, from 2015 to 2021, were the warmest on record. Last year was the fifth or seventh warmest on record around the world. The average worldwide temperature in 2021 was roughly 1.11 degrees Celsius higher than the “pre-industrial average” of world temperatures between 1850 and 1900.
In 2021, sea levels also reached a new peak. Between 2013 and 2021, the global average annual rise in sea level was 4.5mm.
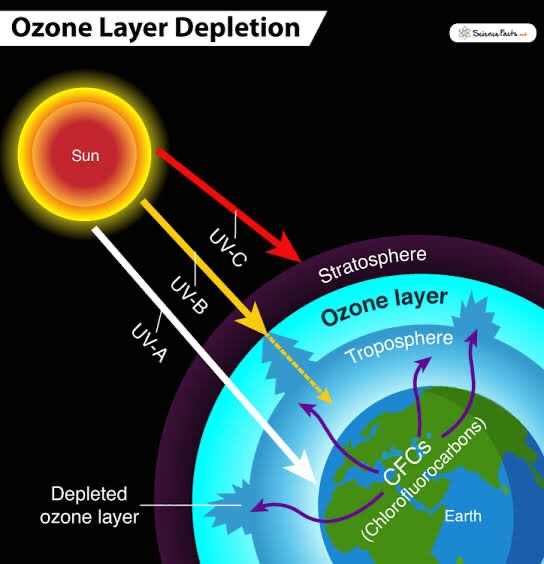
According to the WMO, the ozone hole over the Antarctic in 2021 was “bigger and deeper” than 70% of the ozone holes detected since 1979. In October, it grew to its largest size of the year, covering 24.8 million km2. Colder-than-average conditions in the stratosphere – the second layer of the Earth’s atmosphere from ground level – caused it, according to the WMO. Another important contributor was a powerful polar vortex, which is a belt of frigid air around the Earth’s North Pole.
Rainfall was recorded for the first time on Greenland’s ice sheet at its highest point. Summit Station is a research station located over 3,200 meters above sea level.
On August 14, 2021, Summit Station had several hours of rain. For almost nine hours, the air temperature remained above freezing. According to the WMO, this was part of an “extraordinary” mid-August melt episode for Greenland, which was caused by a mass of warm, humid air.

According to the State of the Global Climate 2021, “extreme heat waves” broke records in western North America and the Mediterranean. When the temperature in Death Valley, California, reached 54.4°C on July 9, 2021, it was the world’s highest temperature since at least the 1930s. On August 11, a research station near Syracuse, Sicily, set a new temporary European record with a temperature of 48.8°C.
Tunisia’s Kairouan hit a new high of 50.3°C. Spain and Turkey both set new national records, with temperatures of 47.4°C in Montoro, Spain, and 49.1°C in Cizre, Turkey, near the Syrian border.
According to the World Meteorological Organization, Hurricane Ida made landfall in Louisiana on August 29, 2017, with winds of 240 kilometers per hour, matching the state’s strongest landfall ever. Ida was the most powerful hurricane of the North Atlantic season, producing significant wind damage and storm surge flooding. Hurricane Sandy generated $75 billion in economic losses in the United States and is responsible for 115 deaths in the United States and Venezuela. In 2021, there were 21 named storms, far more than the average of 14 per year between 1981 and 2010, according to the WMO.
Western Europe had some of the greatest floodings it has ever seen in mid-July 2021. The worst hit areas were western Germany and eastern Belgium. In Hagen, West Germany, 241mm of rain fell in 22 hours. Rivers overflowed, some towns were flooded, and landslides occurred. Germany had 183 deaths, whereas Belgium had 36. Flooding is estimated to have cost Germany $20 billion in lost revenue. Flooding was particularly severe in France, the Netherlands, Luxembourg, and Switzerland.
Drought has caused Lake Mead, a reservoir on the Colorado River in the Southwest United States, to reach a new low water level.
The reservoir was 47 meters below full capacity in July, the lowest level ever recorded. Other countries affected by the drought include Iran, Pakistan, Afghanistan, Turkey, and Turkmenistan. Due to the extreme drought in Canada, harvest levels for wheat and canola – a crop used to make cooking oil and animal feed – were projected to be 35 percent to 40% lower than in 2020.

