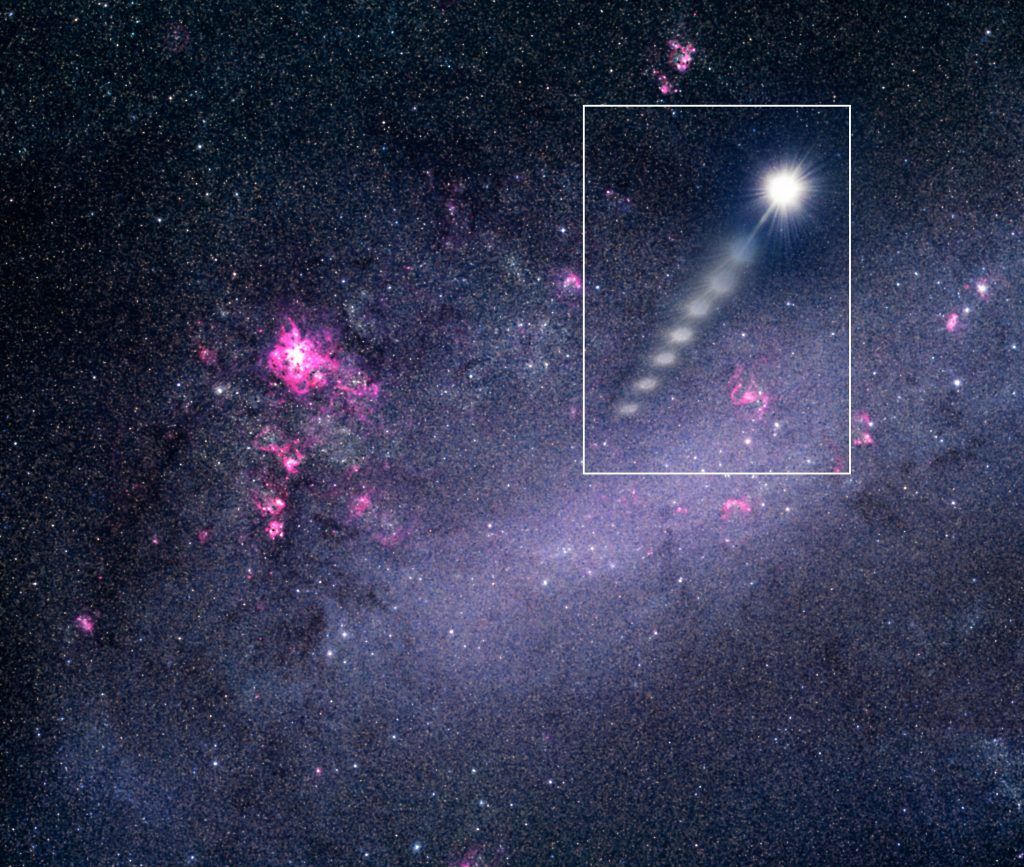
The Milky Way is being raced by six new speeding stars recently identified.
The super-speedy stars J0927 and J1235 are traveling twice as quickly as any previously seen object of this kind. New findings reveal that these extraordinary celestial objects are currently racing through space with astonishing velocities: one star is soaring at a mind-boggling rate of 5.1 million miles per hour (equivalent to 2,285 kilometers per second), while the other is hurtling at an impressive speed of 3.8 million miles per hour (approximately 1,694 kilometers per second).
If J0927 were a terrestrial object, it could travel in less than a second from New York to Mississippi due to its record-breaking sun-orbiting velocity. A moving object could complete 694 orbits of the planet in an hour traveling at that speed.
With a combined speed of over 2.2 million miles per hour (1,000 kilometers per second), the other four stars are also not slow movers. As a result of their rapid motion through the Milky Way, these hypervelocity stars have reached what is known as their escape velocity, which is the velocity required to escape the gravitational pull of our galaxy. The Milky Way is being crossed by these stars far more swiftly than it would be by other stars, which makes them special. According to team head and Harvard/Smithsonian Centre for Astrophysics researcher Kareem El-Badry, “They’ll be blasted into intergalactic space shortly because they’re quicker than the galactic escape velocity.
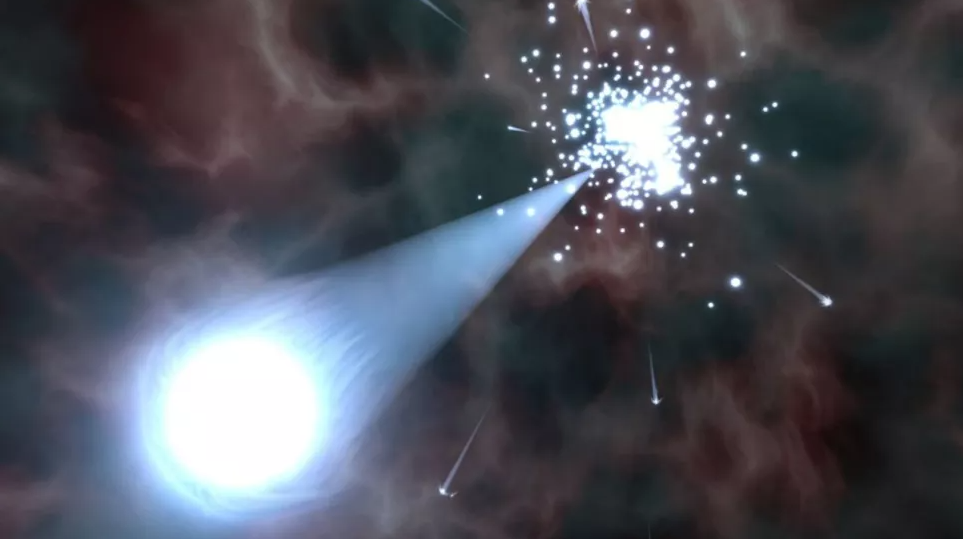

The discovery team speculates that the extraordinary velocity of these four stars may have been caused by their launch by a specific kind of cosmic explosion known as a Type Ia supernova. They also experienced unusually high surface temperatures as a result, which El-Badry claimed startled the researchers. The astronomer added that they are also much hotter than typical stars, which is probably due to the peculiar way in which they formed, which included a supernova explosion right next to them.
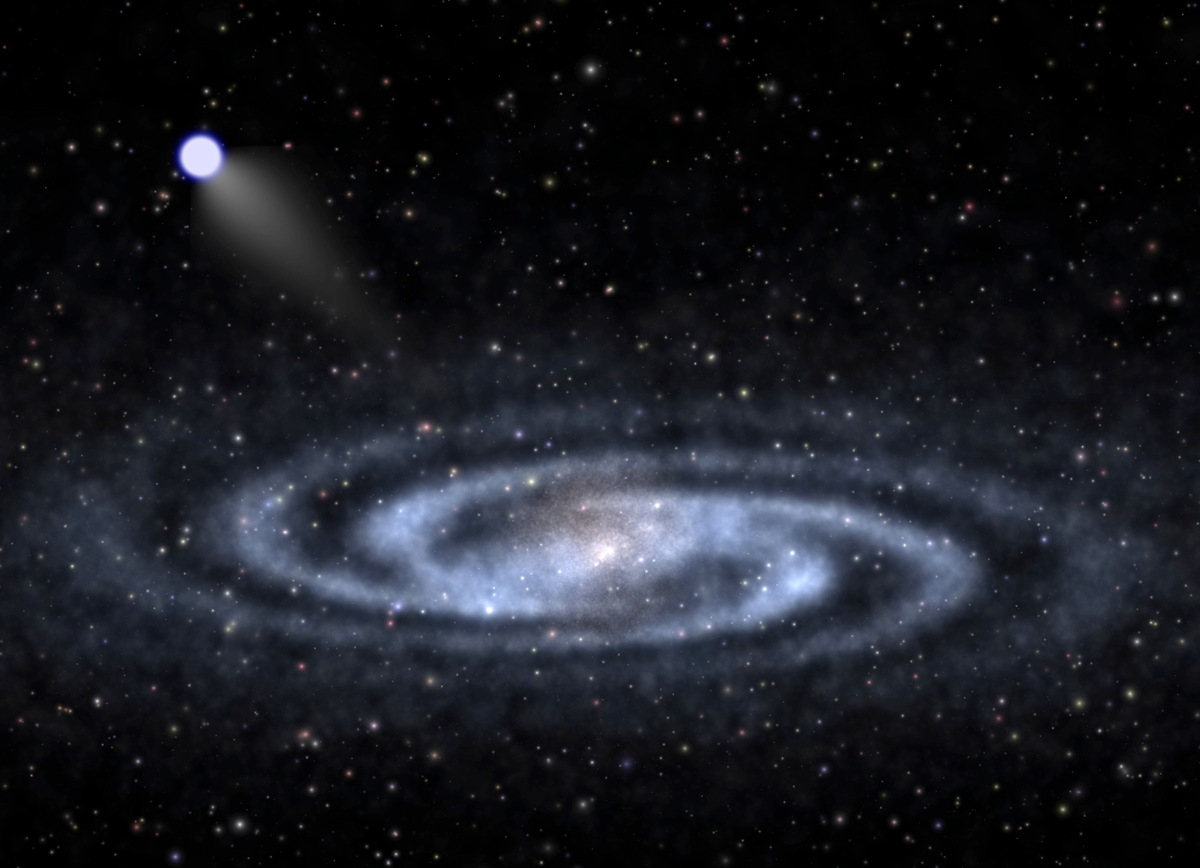

White dwarfs, stellar remnants that arise when stars like the sun die by consuming matter from a partner star, are examples of binary systems that contain type Ia supernovas.
Mysterious Black Hole Discovered by Researchers – ‘a Needle in a Haystack’
White dwarfs, also known as “degenerate stars,” are extremely dense as a result of being formed from the collapse of a stellar core with a mass roughly equal to that of the sun compressed into an Earth-sized sphere, but they aren’t massive enough to cross the so-called Chandrasekhar limit, which is the mass a star needs to reach before it can produce a “normal” supernova and a neutron star or even a black hole when it dies.


