Analysis suggests that Bengaluru and Gurugram, two of India’s digital development centers, are at the heart of this activity. India is currently dealing with a three-and-a-half-year spike in cybercrime.
The Future Crime Research Foundation (FCRF), a nonprofit organization, highlighted cybercrime hotspots from January 2020 to June 2023 in its paper titled “A Deep Dive into Cybercrime Trends Impacting India.” Examining the ten Indian regions most vulnerable to cybercrime reveals common elements that increase their susceptibility. According to the paper, these factors include proximity to large urban centers geographically, a lack of adequate cybersecurity infrastructure, socioeconomic difficulties, and low levels of digital literacy.

Tech hubs are located in some of the regions with the highest cybercrime rates. Inaccurate justifications were given for including Gurugram and Bangalore, both top-five destinations in Asia for the IT industry. On FCRF’s list, the Gurugram neighborhood, which is home to the identically named projected IT city, ranked at number six. Despite having a population of less than 0.2 percent in India, the district was responsible for 8.1% of recorded cybercrime. The FCRF stated that this could be attributed to its standing as a major corporate and IT center, making it an appealing target for cybercriminals seeking valuable data or financial benefits.
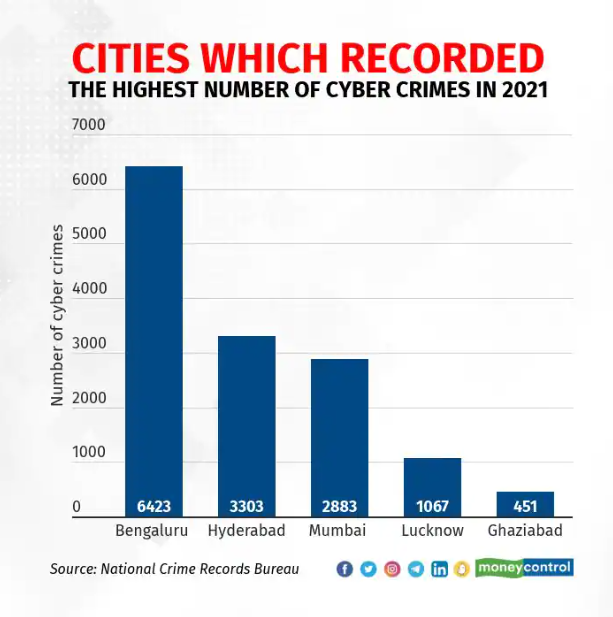
The neighborhood houses many call centers and outsourcing businesses. The city is home to numerous well-known tech companies, including Google, Microsoft, IBM India, Accenture, Cognizant, Infosys, Wipro, and more. Although the city is reputed to have the third-highest per capita GDP in India, the Foundation indicated that “disparities in digital literacy and cybersecurity knowledge” may be variables influencing criminal behavior. FCRF has pinpointed Bangalore, situated within the Karnataka region, as a recently identified hub for cybercrime. The city is often referred to as the “Silicon Valley of India” due to the abundance of IT companies that call it home, including Infosys, Wipro, Tata Consultancy Services, IBM India, Microsoft, Google, Amazon, Intel, Cisco, Samsung Research Institute, and more. Bharatpur, a neighboring city of Gurugram, topped the list with 18% of all cybercrime in India.

Apart from housing major metropolitan areas such as Delhi and Jaipur, FCRF also associates the elevated crime rate in the region with a shortage of digital skills and limited employment prospects. Mathura, which houses numerous important holy sites, came in second with 12%. The FCRF pointed to a lack of cybersecurity infrastructure and the area’s popularity as a tourist destination as possible explanations for the prevalence of cybercrimes there. Unified Payments Interface (UPI) fraud accounted for over half (47.25 percent) of all reported cybercrimes in India, according to another statistic in the survey. Fraud involving debit, credit, and SIM cards lagged at 11.27 percent. Altogether, 77.41% of instances comprised criminal actions driven by the desire for monetary profit.


